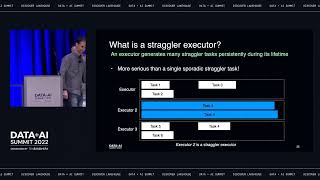
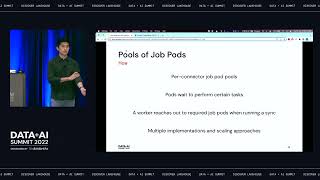
Since the general availability of Apache Spark’s native support for running on Kubernetes with Spark 3.1 in March 2021, the Spark community is increasingly choosing to run on k8s to benefit of containerization, efficient resource-sharing, and the tools from the cloud-native ecosystem.
Data teams are faced with complexities in this transition, including how to leverage spot VMs. These instances enable up to 90% cost savings but are not guaranteed to be available and face the risk of termination. This session will cover concrete guidelines on how to make Spark run reliably on spot instances, with code examples from real-world use cases.
Main topics: • Using spot nodes for Spark executors • Mixing instance types & sizes to reduce risk of spot interruptions - cluster autoscaling • Spark 3.0: Graceful Decommissioning - preserve shuffle files on executor shutdown • Spark 3.1: PVC reuse on executor restart - disaggregate compute & shuffle storage • What to look for in future Spark releases
Connect with us: Website: https://databricks.com Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/databricksinc Twitter: https://twitter.com/databricks LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/data... Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/databricksinc/