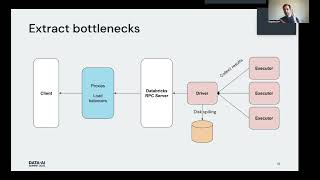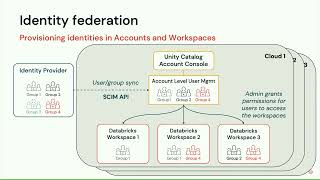
Across industries, a multicloud setup has quickly become the reality for large organizations. Multi-cloud introduces new governance challenges as permissions models often do not translate from one cloud to the other and if they do, are insufficiently granular to accommodate privacy requirements and principles of least privilege. This problem can be especially acute for data and AI workloads that rely on sharing and aggregating large and diverse data sources across business unit boundaries and where governance models need to incorporate assets such as table rows/columns and ML features and models.
In this session, we will provide guidelines on how best to overcome these challenges for companies that have adopted the Databricks Lakehouse as their collaborative space for data teams across the organization, by exploiting some of the unique product features of the Databricks platform. We will focus on a common scenario: a data platform team providing data assets to two different ML teams, one using the same cloud and the other one using a different cloud.
We will explain the step-by-step setup of a unified governance model by leveraging the following components and conventions:
- Unity Catalog for implementing fine-grained access control across all data assets: files in cloud storage, rows and columns in tables and ML features and models
- The Databricks Terraform provider to automatically enforce guardrails and permissions across clouds
- Account level SSO Integration and identity federation to centralize administer access across workspaces
- Delta sharing to seamlessly propagate changes in provider data sets to consumers in near real-time
- Centralized audit logging for a unified view on what asset was accessed by whom
Talk by: Ioannis Papadopoulos and Volker Tjaden
Connect with us: Website: https://databricks.com Twitter: https://twitter.com/databricks LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/databricks Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/databricksinc Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/databricksinc