
 talk-data.com
talk-data.com
Topic
Docker
7
tagged
Activity Trend
Top Events


Autonomous AI agents are transforming industries by enabling systems to perform tasks, make decisions and adapt in real time without human intervention. In this talk, I will delve into the architecture and design principles required to build these agents within scalable AI infrastructure. Key topics will include constructing modular, reusable frameworks, optimizing resource allocation and enabling interoperability between agents and data pipelines. I will discuss practical use cases in which attendees will learn how to leverage containerization and orchestration techniques to enhance the flexibility and performance of these agents while ensuring low-latency decision-making. This session will also highlight challenges like ensuring robustness, ethical considerations and strategies for real-time feedback loops. Participants will gain actionable insights into building autonomous AI agents that drive efficiency, scalability and innovation in modern AI ecosystems.
It's finally possible to bring the awesome power of Large Language Models (LLMs) to your laptop. This talk will explore how to run and leverage small, openly available LLMs to power common tasks involving data, including selecting the right models, practical use cases for running small models, and best practices for deploying small models effectively alongside databases.
Bio: Jeffrey Morgan is the founder of Ollama, an open-source tool to get up and run large language models. Prior to founding Ollama, Jeffrey founded Kitematic, which was acquired by Docker and evolved into Docker Desktop. He has previously worked at companies including Docker, Twitter, and Google.
➡️ Follow Us LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/small-data-sf/ X/Twitter : https://twitter.com/smalldatasf Website: https://www.smalldatasf.com/
Discover how to run large language models (LLMs) locally using Ollama, the easiest way to get started with small AI models on your Mac, Windows, or Linux machine. Unlike massive cloud-based systems, small open source models are only a few gigabytes, allowing them to run incredibly fast on consumer hardware without network latency. This video explains why these local LLMs are not just scaled-down versions of larger models but powerful tools for developers, offering significant advantages in speed, data privacy, and cost-effectiveness by eliminating hidden cloud provider fees and risks.
Learn the most common use case for small models: combining them with your existing factual data to prevent hallucinations. We dive into retrieval augmented generation (RAG), a powerful technique where you augment a model's prompt with information from a local data source. See a practical demo of how to build a vector store from simple text files and connect it to a model like Gemma 2B, enabling you to query your own data using natural language for fast, accurate, and context-aware responses.
Explore the next frontier of local AI with small agents and tool calling, a new feature that empowers models to interact with external tools. This guide demonstrates how an LLM can autonomously decide to query a DuckDB database, write the correct SQL, and use the retrieved data to answer your questions. This advanced tutorial shows you how to connect small models directly to your data engineering workflows, moving beyond simple chat to create intelligent, data-driven applications.
Get started with practical applications for small models today, from building internal help desks to streamlining engineering tasks like code review. This video highlights how small and large models can work together effectively and shows that open source models are rapidly catching up to their cloud-scale counterparts. It's never been a better time for developers and data analysts to harness the power of local AI.

ABOUT THE TALK: In this talk, Erik Bernhardsson will share how Modal starts 1000s of large containers in seconds, and what they had to do under the surface to build this. This includes a custom file system written in Rust, their own container runtime, and their own container image builder. This talk will give you an idea of how containers work along with some of the low-level Linux details underneath. We'll also talk about many infrastructure tools hold data teams back, and why they deserve faster and better tools.
ABOUT THE SPEAKER: Erik Bernhardsson is the founder and CEO of Modal, which is an infrastructure provider for data teams. Before Modal, Erik was the CTO at Better for six years, and previously spent seven years at Spotify, building the music recommendation system and running data teams.
ABOUT DATA COUNCIL: Data Council (https://www.datacouncil.ai/) is a community and conference series that provides data professionals with the learning and networking opportunities they need to grow their careers.
Make sure to subscribe to our channel for the most up-to-date talks from technical professionals on data related topics including data infrastructure, data engineering, ML systems, analytics and AI from top startups and tech companies.
FOLLOW DATA COUNCIL: Twitter: https://twitter.com/DataCouncilAI LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/datacouncil-ai/

Since the general availability of Apache Spark’s native support for running on Kubernetes with Spark 3.1 in March 2021, the Spark community is increasingly choosing to run on k8s to benefit of containerization, efficient resource-sharing, and the tools from the cloud-native ecosystem.
Data teams are faced with complexities in this transition, including how to leverage spot VMs. These instances enable up to 90% cost savings but are not guaranteed to be available and face the risk of termination. This session will cover concrete guidelines on how to make Spark run reliably on spot instances, with code examples from real-world use cases.
Main topics: • Using spot nodes for Spark executors • Mixing instance types & sizes to reduce risk of spot interruptions - cluster autoscaling • Spark 3.0: Graceful Decommissioning - preserve shuffle files on executor shutdown • Spark 3.1: PVC reuse on executor restart - disaggregate compute & shuffle storage • What to look for in future Spark releases
Connect with us: Website: https://databricks.com Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/databricksinc Twitter: https://twitter.com/databricks LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/data... Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/databricksinc/
Elixir is an Erlang-VM bytecode-compatible programming language that is growing in popularity.
In this session I will show how you can apply Elixir towards solving data engineering problems in novel ways.
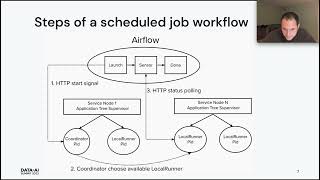
Examples include: • How to leverage Erlang's lightweight distributed process coordination to run clusters of workers across docker containers and perform data ingestion. • A framework that hooks Elixir functions as steps into Airflow graphs. • How to consume and process Kafka events directly within Elixir microservices.
For each of the above I'll show real system examples and walk through the key elements step by step. No prior familiarity with Erlang or Elixir will be required.
Connect with us: Website: https://databricks.com Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/databricksinc Twitter: https://twitter.com/databricks LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/data... Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/databricksinc/

It's finally possible to bring the awesome power of Large Language Models (LLMs) to your laptop. This talk will explore how to run and leverage small, openly available LLMs to power common tasks involving data, including selecting the right models, practical use cases for running small models, and best practices for deploying small models effectively alongside databases.
Bio: Jeffrey Morgan is the founder of Ollama, an open-source tool to get up and run large language models. Prior to founding Ollama, Jeffrey founded Kitematic, which was acquired by Docker and evolved into Docker Desktop. He has previously worked at companies including Docker, Twitter, and Google.
➡️ Follow Us LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/small-data-sf/ X/Twitter : https://twitter.com/smalldatasf Website: https://www.smalldatasf.com/
Discover how to run large language models (LLMs) locally using Ollama, the easiest way to get started with small AI models on your Mac, Windows, or Linux machine. Unlike massive cloud-based systems, small open source models are only a few gigabytes, allowing them to run incredibly fast on consumer hardware without network latency. This video explains why these local LLMs are not just scaled-down versions of larger models but powerful tools for developers, offering significant advantages in speed, data privacy, and cost-effectiveness by eliminating hidden cloud provider fees and risks.
Learn the most common use case for small models: combining them with your existing factual data to prevent hallucinations. We dive into retrieval augmented generation (RAG), a powerful technique where you augment a model's prompt with information from a local data source. See a practical demo of how to build a vector store from simple text files and connect it to a model like Gemma 2B, enabling you to query your own data using natural language for fast, accurate, and context-aware responses.
Explore the next frontier of local AI with small agents and tool calling, a new feature that empowers models to interact with external tools. This guide demonstrates how an LLM can autonomously decide to query a DuckDB database, write the correct SQL, and use the retrieved data to answer your questions. This advanced tutorial shows you how to connect small models directly to your data engineering workflows, moving beyond simple chat to create intelligent, data-driven applications.
Get started with practical applications for small models today, from building internal help desks to streamlining engineering tasks like code review. This video highlights how small and large models can work together effectively and shows that open source models are rapidly catching up to their cloud-scale counterparts. It's never been a better time for developers and data analysts to harness the power of local AI.