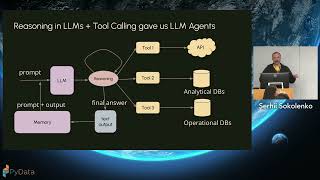
Artificial intelligence is entering a new phase. No longer limited to answering prompts or completing simple writing tasks, AI agents can now reason, plan, and act with increasing independence. From accelerating scientific breakthroughs to supporting creative work, these systems are quickly reshaping industries and everyday life. This book provides the conceptual foundation and practical insights you need to understand—and effectively work with—this emerging technology. Through hundreds of clear graphic illustrations, Maarten Grootendorst and Jay Alammar explain how AI agents are built, how they think, and where they're heading. Designed for professionals, students, and curious learners alike, this guide goes beyond the buzz to reveal what's actually happening inside these systems, why it matters, and how to apply the knowledge in real-world contexts. With its visual storytelling and accessible explanations, An Illustrated Guide to AI Agents is your essential reference for navigating the next frontier of artificial intelligence. Explore the core architecture of AI agents: tools, memory, and planning Understand reasoning LLMs, multimodal models, and multi-agent collaboration Learn advanced methods, including distillation, quantization, and reinforcement learning Evaluate real-world applications, strengths, and limitations of AI agents