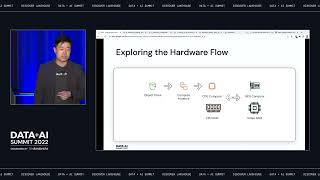
Delta Lake is an open-source storage format that can be ideally used for storing large-scale datasets, which can be used for single-node and distributed training of deep learning models. Delta Lake storage format gives deep learning practitioners unique data management capabilities for working with their datasets. The challenge is that, as of now, it’s not possible to use Delta Lake to train PyTorch models directly.
PyTorch community has recently introduced a Torchdata library for efficient data loading. This library supports many formats out of the box, but not Delta Lake. This talk will demonstrate using the Delta Lake storage format for single-node and distributed PyTorch training using the torchdata framework and standalone delta-rs Delta Lake implementation.
Talk by: Michael Shtelma
Connect with us: Website: https://databricks.com Twitter: https://twitter.com/databricks LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/databricks Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/databricksinc Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/databricksinc