The explosive growth of cloud data—and its importance for analytics and AI—demands a new approach to protection and access. Traditional backup tools weren’t built to handle hyperscale workloads, such as Azure Blob Storage and Cosmos DB, resulting in costly silos. Discover how a cloud-native platform delivers hyperscale protection, automates operations, reduces TCO, and turns backups into a live, queryable data lake for analytics in Azure Synapse, Microsoft Fabric, and Azure OpenAI.
 talk-data.com
talk-data.com
Topic
Data Lake
311
tagged
Activity Trend
Top Events
DuckDB is the best way to execute SQL on a single node. But with its embedding-friendly nature, it makes an excellent foundation for building distributed systems. George Fraser, CEO of Fivetran, will tell us how Fivetran used DuckDB to power its Iceberg data lake writer—coordinating thousands of small, parallel tasks across a fleet of workers, each running DuckDB queries on bounded datasets. The result is a high-throughput, dual-format (Iceberg + Delta) data lake architecture where every write scales linearly, snapshots stay perfectly in sync, and performance rivals a commercial database while remaining open and portable.
Learn how the Wikimedia Foundation implemented an on-prem, open source data lake to fund Wikipedia and the future of open knowledge. We'll discuss data architecture including challenges integrating open source tools, learnings from our implementation, how we achieved a 10x decrease in query run times, and more.
Apache Iceberg™ fournit une norme de stockage ouverte qui peut démocratiser vos données stockées dans des data lakes distincts en offrant la liberté et l'interopérabilité d'utiliser divers moteurs de traitement de données. Rejoignez cette session pour explorer les dernières avancées de Snowflake pour le data engineering sur les tables Iceberg de Snowflake. Nous plongerons dans les fonctionnalités récemment lancées qui améliorent l'interopérabilité et apportent la facilité d'utilisation de Snowflake à vos data lakes Iceberg.
L'explosion des données IoT dans les environnements industriels nécessite des architectures de données robustes et évolutives. Cette présentation explore comment les data lakes, et plus spécifiquement l'architecture Lakehouse, répondent aux défis du stockage et du traitement de volumes massifs de données IoT hétérogènes.
À travers l'exemple concret du monitoring opérationnel d'un parc éolien offshore, nous démontrerons comment une solution Lakehouse permet de gérer efficacement les flux de données haute fréquence provenant de capteurs industriels. Nous détaillerons le processus complet : de l'ingestion des données de télémétrie en temps réel au déploiement de modèles de maintenance prédictive, en passant par l'entraînement d'algorithmes de détection d'anomalies et de forecasting.
Cette étude de cas illustrera les avantages clés du data lake pour l'IoT industriel : flexibilité de stockage multi-formats, capacité de traitement en temps réel et en batch, intégration native des outils de machine learning, et optimisation des coûts opérationnels. L'objectif est de fournir un retour d'expérience pratique sur l'implémentation de cette architecture dans un contexte d'Asset Integrity Management, applicable à de nombreux secteurs industriels.
Une part essentielle des données stratégiques réside dans des systèmes critiques et de production (tels que IBM i, Oracle, SAP, SQL Server...) . Les extraire sans perturber la production est l’un des obstacles majeurs aux initiatives de modernisation.
Cette démonstration montrera comment la réplication de données permet de :
• Diffuser la donnée en temps réel sans impact sur les opérations,
• Consolider les données dans Snowflake, BigQuery ou les Data Lake pour l’analyse et l’IA,
• Réduire les coûts d’intégration et limiter les risques projets.
Une session de 30 minutes avec démonstration et temps de questions-réponses.
Les projets en intelligence artificielle et en machine learning nécessitent un accès à des données centralisées et de haute qualité. Pourtant, gérer des pipelines de données en interne conduit souvent à une complexité accrue, des inefficacités et des retards qui freinent l’innovation. Cette session montrera comment l’automatisation transforme la circulation des données, en simplifiant l’ingestion, la normalisation et la préparation, pour alimenter efficacement les applications d’IA et de ML.
Vous découvrirez comment des pipelines automatisés, des services de data lake managés et des modèles de déploiement rapides permettent de passer plus vite de l’expérimentation à la production, en générant une réelle valeur business.
Au programme :
● Stratégies pour centraliser et normaliser des données issues de sources diverses
● Comment obtenir des données fiables et de haute qualité grâce à l’automatisation
● Les leviers pour accélérer le passage de l’IA de l’expérimentation à la production grâce à des flux de données évolutifs
● Démonstration Live: Découvrez en direct comment construire une application GenAI et créer un chatbot capable de fournir des recommandations personnalisées – une illustration concrète de la valeur apportée par des données centralisées et fiables.
De la centralisation à l’agilité : le Data Mesh à La Centrale
• Comment une marketplace auto leader est passée du Data Lake aux Data Products pour accélérer l’innovation.
• Les outils et pratiques pour accompagner les équipes dans cette transformation
• Retours concrets : qualité des données, gouvernance distribuée, nouveaux rôles et autonomie des feature teams.
• Une approche pragmatique, incrémentale… avec déjà des impacts visibles sur le business et les produits.
Learn how Trade Republic builds its analytical data stack as a modern, real-time Lakehouse with ACID guarantees. Using Debezium for change data capture, we stream database changes and events into our data lake. We leverage Apache Iceberg to ensure interoperability across our analytics platform, powering operational reporting, data science, and executive dashboards.
Construisez des agents business avec une vrai logique métier dans l'écosysteme Google Cloud. On vous montrera comment un agent peut se déployer à l'échelle et peut interagir avec des progiciels des bases de données, voir même data lake de votre SI !
As organizations increasingly adopt data lake architectures, analytics databases face significant integration challenges beyond simple data ingestion. This talk explores the complex technical hurdles encountered when building robust connections between analytics engines and modern data lake formats.
We'll examine critical implementation challenges, including the absence of native library support for formats like Delta Lake, which necessitates expansion into new programming languages such as Rust to achieve optimal performance. The session explores the complexities of managing stateful systems, addressing caching inconsistencies, and reconciling state across distributed environments.
A key focus will be on integrating with external catalogs while maintaining data consistency and performance - a challenge that requires careful architectural decisions around metadata management and query optimization. We'll explore how these technical constraints impact system design and the trade-offs involved in different implementation approaches.
Attendees will gain a practical understanding of the engineering complexity behind seamless data lake integration and actionable approaches to common implementation obstacles.
How to move data from thousands of SQL databases to data lake with no impact on OLTP? We'll explore the challenges we faced while migrated legacy batch data flows to event-based architecture. A key challenge for our data engineers was the multi-tenant architecture of our backend, meaning that we had to handle the same SQL schema on over 15k databases. We'll present the journey employing Debezium, Azure Event Hub, Delta Live tables and the extra tooling we had to put in place.
In this session, Paul Wilkinson, Principal Solutions Architect at Redpanda, will demonstrate Redpanda's native Iceberg capability: a game-changing addition that bridges the gap between real-time streaming and analytical workloads, eliminating the complexity of traditional data lake architectures while maintaining the performance and simplicity that Redpanda is known for.
Paul will explore how this new capability enables organizations to seamlessly transition streaming data into analytical formats without complex ETL pipelines or additional infrastructure overhead in a follow-along demo - allowing you to build your own streaming lakehouse and show it to your team!
So you’ve heard of Databricks, but still not sure what the fuss is all about. Yes you’ve heard it’s Spark, but then there’s this Delta thing that’s both a data lake and a data warehouse (isn’t that what Iceberg is?) And then there's Unity Catalog, that's not just a catalog, it also does access management but even surprising things like optimise your data and programmatic access to lineage and billing? But then serverless came out and now you don’t even have to learn Spark? And of course there’s a bunch of AI stuff to use or create yourself. So why not spend 30 mins learning the details of what Databricks does, and how it can turn you into a rockstar Data Engineer.
It’s now over six years since the emergence of the paper "How to Move Beyond a Monolithic Data Lake to a Distributed Data Mesh” by Zhamak Dehghani that had a major impact on the data and analytics industry.
It highlighted major data architecture failures and called for a rethink in data architecture and in data provisioning by creating a data supply chain and democratising data engineering to enable business domain-oriented creation of reusable data products to make data products available as self-governing services.
Since then, we have seen many companies adopt Data Mesh strategies, and the repositioning of some software products as well as the emergence of new ones to emphasize democratisation. But is what has happened since totally addressing the problems that Data Mesh was intending to solve? And what new problems are arising as organizations try to make data safely available to AI projects at machine-scale?
In this unmissable session Big Data LDN Chair Mike Ferguson sits down with Zhamak Dehghani to talk about what has happened since Data Mesh emerged. It will look at:
● The drivers behind Data Mesh
● Revisiting Data Mesh to clarify on what a data product is and what Data Mesh is intending to solve
● Did data architecture really change or are companies still using existing architecture to implement this?
● What about technology to support this - Is Data Fabric the answer or best of breed tools?
● How critical is organisation to successful Data Mesh implementation
● Roadblocks in the way of success e.g., lack of metadata standards
● How does Data Mesh impact AI?
● What’s next on the horizon?
Discover how Apache Airflow powers scalable ELT pipelines, enabling seamless data ingestion, transformation, and machine learning-driven insights. This session will walk through: Automating Data Ingestion: Using Airflow to orchestrate raw data ingestion from third-party sources into your data lake (S3, GCP), ensuring a steady pipeline of high-quality training and prediction data. Optimizing Transformations with Serverless Computing: Offloading intensive transformations to serverless functions (GCP Cloud Run, AWS Lambda) and machine learning models (BigQuery ML, Sagemaker), integrating their outputs seamlessly into Airflow workflows. Real-World Impact: A case study on how INTRVL leveraged Airflow, BigQuery ML, and Cloud Run to analyze early voting data in near real-time, generating actionable insights on voter behavior across swing states. This talk not only provides a deep dive into the Political Tech space but also serves as a reference architecture for building robust, repeatable ELT pipelines. Attendees will gain insights into modern serverless technologies from AWS and GCP that enhance Airflow’s capabilities, helping data engineers design scalable, cloud-agnostic workflows.
SumUp's Data Lake journey.
Discussion on how dbt powers the AI-ready data lake.
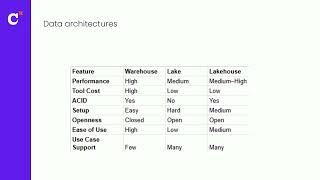
Data lakehouses continue to be hyped but do they replace or complement data lakes and data warehouses? Where do we stand from an architectural perspective? What is hype and what is real? What should be expected in the coming years?

Navy Federal Credit Union has 200+ enterprise data sources in the enterprise data lake. These data assets are used for training 100+ machine learning models and hydrating a semantic layer for serving, at an average 4,000 business users daily across the credit union. The only option for extracting data from analytic semantic layer was to allow consuming application to access it via an already-overloaded cloud data warehouse. Visualizing data lineage for 1,000 + data pipelines and associated metadata is impossible and understanding the granular cost for running data pipelines is a challenge. Implementing Unity Catalog opened alternate path for accessing analytic semantic data from lake. It also opened the doors to remove duplicate data assets stored across multiple lakes which will save hundred thousands of dollars in data engineering efforts, compute and storage costs.