LLMs seem like a hot solution now, until you try deploying one. In this episode, Andriy Burkov, machine learning expert and author of The Hundred-Page Machine Learning Book, joins us for a grounded, sometimes blunt conversation about why many LLM applications fail. We talk about sentiment analysis, difficulty with taxonomy, agents getting tripped up on formatting, and why MCP might not solve your problems. If you're tired of the hype and want to understand the real state of applied LLMs, this episode delivers. What You'll Learn: What is often misunderstood about LLMs The reliability of sentiment analysis How can we make agents more resilient? 📚 Check out Andriy's books on machine learning and LLMs: The Hundred-Page Machine Learning Book The Hundred-Page Language Models Book: hands-on with Pytorch 🤝 Follow Andriy on LinkedIn! Register for free to be part of the next live session: https://bit.ly/3XB3A8b Follow us on Socials: LinkedIn YouTube Instagram (Mavens of Data) Instagram (Maven Analytics) TikTok Facebook Medium X/Twitter
 talk-data.com
talk-data.com
Topic
PyTorch
80
tagged
Activity Trend
Top Events

If we want to run data science workloads (e.g. using Tensorflow, PyTorch, and others) in containers (for local development or production on Kubernetes), we need to build container images. Doing that with a Dockerfile is fairly straightforward, but is it the best method? In this talk, we'll take a well-known speech-to-text model (Whisper) and show various ways to run it in containers, comparing the outcomes in terms of image size and build time.

Building and deploying scalable, reproducible machine learning pipelines can be challenging, especially when working with orchestration tools like Slurm or Kubernetes. In this talk, we demonstrate how to create an end-to-end ML pipeline for anomaly detection in International Space Station (ISS) telemetry data using only Python code.
We show how Kubeflow Pipelines, MLFlow, and other open-source tools enable the seamless orchestration of critical steps: distributed preprocessing with Dask, hyperparameter optimization with Katib, distributed training with PyTorch Operator, experiment tracking and monitoring with MLFlow, and scalable model serving with KServe. All these steps are integrated into a holistic Kubeflow pipeline.
By leveraging Kubeflow's Python SDK, we simplify the complexities of Kubernetes configurations while achieving scalable, maintainable, and reproducible pipelines. This session provides practical insights, real-world challenges, and best practices, demonstrating how Python-first workflows empower data scientists to focus on machine learning development rather than infrastructure.
Formation pratique axée sur l’entraînement et l’expérimentation avec des modèles de réseaux neuronaux, explorant TensorFlow et PyTorch.
Formation pratique axée sur l’utilisation et l’expérimentation de modèles de réseaux neuronaux, couvrant l’entraînement et l’expérimentation, avec exercices et démonstrations. Utilisation de TensorFlow, PyTorch et d’autres librairies de machine learning.
Formation immersive et orientée pratique pour créer et déployer un modèle ML capable de prédire le prix d'une voiture, avec manipulation de données et déploiement en production (Python, TensorFlow, PyTorch, Flask, Ngrok).
Formation immersive et orientée pratique sur la création et le déploiement d'une IA capable de prédire le prix d’une voiture. Approche hands-on avec Python, TensorFlow, PyTorch, Flask et Ngrok.
Formation immersive et orientée pratique sur la création et le déploiement d'une IA capable de prédire le prix d'une voiture. Manipulation de données, création d'un modèle de régression, et mise en production avec Python, TensorFlow, PyTorch, Flask et Ngrok. Animation en direct par un formateur expert, approche interactive et pratique.
Formation pratique guidée par un formateur expert. Manipuler des données, créer un modèle de régression et le mettre en production avec Python, TensorFlow, PyTorch, Flask et Ngrok. Approche progressive et interactive pour transformer vos compétences en programmation en solutions d’IA.
Formation pratique de deep learning offrant une introduction claire à l’entraînement et à l’expérimentation avec des modèles de réseaux neuronaux. Combinaison de théorie essentielle et de mises en pratique interactives pour explorer les concepts fondamentaux, tester différentes architectures et ajuster les hyperparamètres afin de comprendre leur impact sur les performances.
Formation pratique sur le deep learning couvrant l’entraînement et l’expérimentation avec des modèles de réseaux neuronaux, exploration des concepts fondamentaux, test d’architectures et ajustement d’hyperparamètres, avec TensorFlow et PyTorch. Durée 6 heures; session animée en direct par un formateur expert.
PyTorch has become the de facto standard for development and research in deep learning. Among the many factors contributing to its popularity is the wide array of customization hooks it provides. These extension mechanisms allow developers to build new functionality on top of PyTorch while maintaining compatibility with its core backend features—a powerful capability for engineers, researchers, and curious hackers, both in-core and downstream. In this talk, we’ll explore various ways to extend PyTorch and present concrete examples of these techniques in action.
GBNet
Gradient Boosting Machines (GBMs) are widely used for their predictive power and interpretability, while Neural Networks offer flexible architectures but can be opaque. GBNet is a Python package that integrates XGBoost and LightGBM with PyTorch. By leveraging PyTorch’s auto-differentiation, GBNet enables novel architectures for GBMs that were previously exclusive to pure Neural Networks. The result is a greatly expanded set of applications for GBMs and an improved ability to interpret expressive architectures due to the use of GBMs.

Eager to learn AI and machine learning but unsure where to start? Laurence Moroney's hands-on, code-first guide demystifies complex AI concepts without relying on advanced mathematics. Designed for programmers, it focuses on practical applications using PyTorch, helping you build real-world models without feeling overwhelmed. From computer vision and natural language processing (NLP) to generative AI with Hugging Face Transformers, this book equips you with the skills most in demand for AI development today. You'll also learn how to deploy your models across the web and cloud confidently. Gain the confidence to apply AI without needing advanced math or theory expertise Discover how to build AI models for computer vision, NLP, and sequence modeling with PyTorch Learn generative AI techniques with Hugging Face Diffusers and Transformers
Scientific researchers need reproducible software environments for complex applications that can run across heterogeneous computing platforms. Modern open source tools, like pixi, provide automatic reproducibility solutions for all dependencies while providing a high level interface well suited for researchers.
This tutorial will provide a practical introduction to using pixi to easily create scientific and AI/ML environments that benefit from hardware acceleration, across multiple machines and platforms. The focus will be on applications using the PyTorch and JAX Python machine learning libraries with CUDA enabled, as well as deploying these environments to production settings in Linux container images.

The last year has seen the rapid progress of Open Source GenAI models and frameworks. This talk covers best practices for custom training and OSS GenAI finetuning on Databricks, powered by the newly announced Serverless GPU Compute. We’ll cover how to use Serverless GPU compute to power AI training/GenAI finetuning workloads and framework support for libraries like LLM Foundry, Composer, HuggingFace, and more. Lastly, we’ll cover how to leverage MLFlow and the Databricks Lakehouse to streamline the end to end development of these models. Key takeaways include: How Serverless GPU compute saves customers valuable developer time and overhead when dealing with GPU infrastructure Best practices for training custom deep learning models (forecasting, recommendation, personalization) and finetuning OSS GenAI Models on GPUs across the Databricks stack Leveraging distributed GPU training frameworks (e.g. Pytorch, Huggingface) on Databricks Streamlining the path to production for these models Join us to learn about the newly announced Serverless GPU Compute and the latest updates to GPU training and finetuning on Databricks!
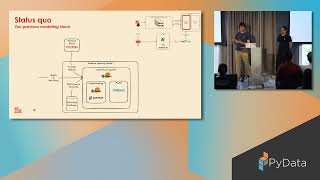
GetYourGuide, a global marketplace for travel experiences, reached diminishing returns with its XGBoost-based ranking system. We switched to a Deep Learning pipeline in just nine months, maintaining high throughput and low latency. We iterated on over 50 offline models and conducted more than 10 live A/B tests, ultimately deploying a PyTorch transformer that yielded significant gains. In this talk, we will share our phased approach—from a simple baseline to a high-impact launch—and discuss the key operational and modeling challenges we faced. Learn how to transition from tree-based methods to neural networks and unlock new possibilities for real-time ranking.

This talk examines multi-threaded parallel inference on PyTorch models using the new No-GIL, free-threaded version of Python. Using a simple 124M parameter GPT2 model that we train from scratch, we explore the novel new territory unlocked by free-threaded Python: parallel PyTorch model inference, where multiple threads, unimpeded by the Python GIL, attempt to generate text from a transformer-based model in parallel.
AI tooling continues to expand with specialized solutions for every step of the development process. For data scientists and engineers, this creates a paradox: more options but potentially more complexity and integration challenges. How do you determine which tools actually improve productivity versus adding unnecessary overhead? Should you prioritize flexibility with individual best-of-breed components or streamline with integrated platforms? What's the most effective way to bridge the gap between experimentation and production-ready AI applications? William Falcon is an AI researcher and the CEO of Lightning AI. He is the creator of PyTorch Lightning, a lightweight framework designed for training models of any size. As the founder of Lightning AI, he leads the development of Lightning AI Studios and the AI Hub. Falcon also shares his expertise in AI research and machine learning engineering through educational content on YouTube and X (formerly Twitter). He is passionate about leveraging AI for social impact. In the episode, Richie and William explore the NY AI hub, the journey from AI idea to production, diverse perspectives in AI development, how Lightning AI simplifies AI workflows, the significance of open-source models, and much more. Links Mentioned in the Show: Lightning AIPyTorch LightningConnect with WilliamCourse: Introduction to Deep Learning in PyTorch CourseRelated Episode: Building Multi-Modal AI Applications with Russ d'Sa, CEO & Co-founder of LiveKitRewatch sessions from RADAR: Skills Edition New to DataCamp? Learn on the go using the DataCamp mobile appEmpower your business with world-class data and AI skills with DataCamp for business
This meetup is a space for developers actively working with any open-source AI libraries, frameworks, or tools, to share their projects, challenges, and solutions. Whether you're building with LangChain, Haystack, Transformers, TensorFlow, PyTorch, or any other open-source AI tool, we want to hear from you. This meetup will provide an opportunity to connect with other developers, share practical tips, and get inspired to build even more with open-source AI on Google Cloud. Come ready to contribute, and let's learn from each other!