Hands-on building a serverless application using AWS Lambda and S3.
 talk-data.com
talk-data.com
Topic
S3
Amazon S3
104
tagged
Activity Trend
Top Events

This IBM Redbooks® publication covers IBM TS7700 R5.3. The IBM TS7700 is part of a family of IBM Enterprise tape products. This book is intended for system architects and storage administrators who want to integrate their storage systems for optimal operation. Building on over 25 years of experience, the R5.3 release includes many features that enable improved performance, usability, and security. Highlights include the IBM TS7700 Advanced Object Store, an all flash TS7770, grid resiliency enhancements, and Logical WORM retention. By using the same hierarchical storage techniques, the TS7700 (TS7770 and TS7760) can also off load to object storage. Because object storage is cloud-based and accessible from different regions, the TS7700 Cloud Storage Tier support essentially allows the cloud to be an extension of the grid. As of this writing, the TS7700C supports the ability to off load to IBM Cloud Object Storage, Amazon S3, and RSTOR. This publication explains features and concepts that are specific to the IBM TS7700 as of release R5.3. The R5.3 microcode level provides IBM TS7700 Cloud Storage Tier enhancements, IBM DS8000 Object Storage enhancements, Management Interface dual control security, and other smaller enhancements. The R5.3 microcode level can be installed on the IBM TS7770 and IBM TS7760 models only. TS7700 provides tape virtualization for the IBM Z® environment. Off loading to physical tape behind a TS7700 is used by hundreds of organizations around the world. New and existing capabilities of the TS7700 5.3 release includes the following highlights: Support for IBM TS1160 Tape Drives and JE/JM media Eight-way Grid Cloud, which consists of up to three generations of TS7700 Synchronous and asynchronous replication of virtual tape and TCT objects Grid access to all logical volume and object data independent of where it resides An all flash TS7770 option for improved performance Full Advanced Object Store Grid Cloud support of DS8000 Transparent Cloud Tier Full AES256 encryption for data that is in-flight and at-rest Tight integration with IBM Z and DFSMS policy management DS8000 Object Store with AES256 in-flight encryption and compression Regulatory compliance through Logical WORM and LWORM Retention support Cloud Storage Tier support for archive, logical volume versions, and disaster recovery Optional integration with physical tape 16 Gb IBM FICON® throughput that exceeds 4 GBps per TS7700 cluster Grid Resiliency Support with Control Unit Initiated Reconfiguration (CUIR) support IBM Z hosts view up to 3,968 3490 devices per TS7700 grid TS7770 Cache On Demand feature that uses capacity-based licensing TS7770 support of SSD within the VED server The TS7700T writes data by policy to physical tape through attachment to high-capacity, high-performance IBM TS1160, IBM TS1150, and IBM TS1140 tape drives that are installed in an IBM TS4500 or TS3500 tape library. The TS7770 models are based on high-performance and redundant IBM Power9® technology. They provide improved performance for most IBM Z tape workloads when compared to the previous generations of IBM TS7700.
Summary
Stream processing systems have long been built with a code-first design, adding SQL as a layer on top of the existing framework. RisingWave is a database engine that was created specifically for stream processing, with S3 as the storage layer. In this episode Yingjun Wu explains how it is architected to power analytical workflows on continuous data flows, and the challenges of making it responsive and scalable.
Announcements
Hello and welcome to the Data Engineering Podcast, the show about modern data management Data lakes are notoriously complex. For data engineers who battle to build and scale high quality data workflows on the data lake, Starburst powers petabyte-scale SQL analytics fast, at a fraction of the cost of traditional methods, so that you can meet all your data needs ranging from AI to data applications to complete analytics. Trusted by teams of all sizes, including Comcast and Doordash, Starburst is a data lake analytics platform that delivers the adaptability and flexibility a lakehouse ecosystem promises. And Starburst does all of this on an open architecture with first-class support for Apache Iceberg, Delta Lake and Hudi, so you always maintain ownership of your data. Want to see Starburst in action? Go to dataengineeringpodcast.com/starburst and get $500 in credits to try Starburst Galaxy today, the easiest and fastest way to get started using Trino. Dagster offers a new approach to building and running data platforms and data pipelines. It is an open-source, cloud-native orchestrator for the whole development lifecycle, with integrated lineage and observability, a declarative programming model, and best-in-class testability. Your team can get up and running in minutes thanks to Dagster Cloud, an enterprise-class hosted solution that offers serverless and hybrid deployments, enhanced security, and on-demand ephemeral test deployments. Go to dataengineeringpodcast.com/dagster today to get started. Your first 30 days are free! Your host is Tobias Macey and today I'm interviewing Yingjun Wu about the RisingWave database and the intricacies of building a stream processing engine on S3
Interview
Introduction How did you get involved in the area of data management? Can you describe what RisingWave is and the story behind it? There are numerous stream processing engines, near-real-time database engines, streaming SQL systems, etc. What is the specific niche that RisingWave addresses?
What are some of the platforms/architectures that teams are replacing with RisingWave?
What are some of the unique capabilities/use cases that RisingWave provides over other offerings in the current ecosystem? Can you describe how RisingWave is architected and implemented?
How have the design and goals/scope changed since you first started working on it? What are the core design philosophies that you rely on to prioritize the ongoing development of the project?
What are the most complex engineering challenges that you have had to address in the creation of RisingWave? Can you describe a typical workflow for teams that are building on top of RisingWave?
What are the user/developer experience elements that you have prioritized most highly?
What are the situations where RisingWave can/should be a system of record vs. a point-in-time view of data in transit, with a data warehouse/lakehouse as the longitudinal storage and query engine? What are the most interesting, innovative, or unexpected ways that you have seen RisingWave used? What are the most interesting, unexpected, or challenging lessons that you have learned while working on RisingWave? When is RisingWave the wrong choice? What do you have planned for the future of RisingWave?
Contact Info
yingjunwu on GitHub Personal Website LinkedIn
Parting Question
From your perspective, what is the biggest gap in the tooling or technology for data management today?
Closing Announcements
Thank you for listening! Don't forget to check out our other shows.

Learn data engineering and modern data pipeline design with AWS in this comprehensive guide! You will explore key AWS services like S3, Glue, Redshift, and QuickSight to ingest, transform, and analyze data, and you'll gain hands-on experience creating robust, scalable solutions. What this Book will help me do Understand and implement data ingestion and transformation processes using AWS tools. Optimize data for analytics with advanced AWS-powered workflows. Build end-to-end modern data pipelines leveraging cutting-edge AWS technologies. Design data governance strategies using AWS services for security and compliance. Visualize data and extract insights using Amazon QuickSight and other tools. Author(s) Gareth Eagar is a Senior Data Architect with over 25 years of experience in designing and implementing data solutions across various industries. He combines his deep technical expertise with a passion for teaching, aiming to make complex concepts approachable for learners at all levels. Who is it for? This book is intended for current or aspiring data engineers, data architects, and analysts seeking to leverage AWS for data engineering. It suits beginners with a basic understanding of data concepts who want to gain practical experience as well as intermediate professionals aiming to expand into AWS-based systems.

With the surge in big data and AI, organizations can rapidly create data products. However, the effectiveness of their analytics and machine learning models depends on the data's quality. Delta Lake's open source format offers a robust lakehouse framework over platforms like Amazon S3, ADLS, and GCS. This practical book shows data engineers, data scientists, and data analysts how to get Delta Lake and its features up and running. The ultimate goal of building data pipelines and applications is to gain insights from data. You'll understand how your storage solution choice determines the robustness and performance of the data pipeline, from raw data to insights. You'll learn how to: Use modern data management and data engineering techniques Understand how ACID transactions bring reliability to data lakes at scale Run streaming and batch jobs against your data lake concurrently Execute update, delete, and merge commands against your data lake Use time travel to roll back and examine previous data versions Build a streaming data quality pipeline following the medallion architecture
GTS Institute : Découvrez la formidable aventure migratoire de "GTS Institute", le Learning Management System interne de l'infrastructure du groupe Société Générale, à partir d'on-premises vers le cloud AWS.

Delta Lake is an open source project that helps implement modern data lake architectures commonly built on cloud storages. With Delta Lake, you can achieve ACID transactions, time travel queries, CDC, and other common use cases on the cloud.
There are a lot of use cases of Delta tables on AWS. AWS has invested a lot in this technology, and now Delta Lake is available with multiple AWS services, such as AWS Glue Spark jobs, Amazon EMR, Amazon Athena, and Amazon Redshift Spectrum. AWS Glue is a serverless, scalable data integration service that makes it easier to discover, prepare, move, and integrate data from multiple sources. With AWS Glue, you can easily ingest data from multiple data sources such as on-prem databases, Amazon RDS, DynamoDB, MongoDB into Delta Lake on Amazon S3 even without expertise in coding.
This session will demonstrate how to get started with processing Delta Lake tables on Amazon S3 using AWS Glue, and querying from Amazon Athena, and Amazon Redshift. The session also covers recent AWS service updates related to Delta Lake.
Talk by: Noritaka Sekiyama and Akira Ajisaka
Here’s more to explore: Why the Data Lakehouse Is Your next Data Warehouse: https://dbricks.co/3Pt5unq Lakehouse Fundamentals Training: https://dbricks.co/44ancQs
Connect with us: Website: https://databricks.com Twitter: https://twitter.com/databricks LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/databricks Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/databricksinc Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/databricksinc

In "Geospatial Data Analytics on AWS," you will learn how to store, manage, and analyze geospatial data effectively using various AWS services. This book provides insight into building geospatial data lakes, leveraging AWS databases, and applying best practices to derive insights from spatial data in the cloud. What this Book will help me do Design and manage geospatial data lakes on AWS leveraging S3 and other storage solutions. Analyze geospatial data using AWS services such as Athena and Redshift. Utilize machine learning models for geospatial data processing and analytics using SageMaker. Visualize geospatial data through services like Amazon QuickSight and OpenStreetMap integration. Avoid common pitfalls when managing geospatial data in the cloud. Author(s) Scott Bateman, Janahan Gnanachandran, and Jeff DeMuth bring their extensive experience in cloud computing and geospatial analytics to this book. With backgrounds in cloud architecture, data science, and geospatial applications, they aim to make complex topics accessible. Their collaborative approach ensures readers can practically apply concepts to real-world challenges. Who is it for? This book is ideal for GIS and data professionals, including developers, analysts, and scientists. It suits readers with a basic understanding of geographical concepts but no prior AWS experience. If you're aiming to enhance your cloud-based geospatial data management and analytics skills, this is the guide for you.
Summary
Data is a team sport, but it's often difficult for everyone on the team to participate. For a long time the mantra of data tools has been "by developers, for developers", which automatically excludes a large portion of the business members who play a crucial role in the success of any data project. Quilt Data was created as an answer to make it easier for everyone to contribute to the data being used by an organization and collaborate on its application. In this episode Aneesh Karve shares the journey that Quilt has taken to provide an approachable interface for working with versioned data in S3 that empowers everyone to collaborate.
Announcements
Hello and welcome to the Data Engineering Podcast, the show about modern data management Truly leveraging and benefiting from streaming data is hard - the data stack is costly, difficult to use and still has limitations. Materialize breaks down those barriers with a true cloud-native streaming database - not simply a database that connects to streaming systems. With a PostgreSQL-compatible interface, you can now work with real-time data using ANSI SQL including the ability to perform multi-way complex joins, which support stream-to-stream, stream-to-table, table-to-table, and more, all in standard SQL. Go to dataengineeringpodcast.com/materialize today and sign up for early access to get started. If you like what you see and want to help make it better, they're hiring across all functions! Your host is Tobias Macey and today I'm interviewing Aneesh Karve about how Quilt Data helps you bring order to your chaotic data in S3 with transactional versioning and data discovery built in
Interview
Introduction How did you get involved in the area of data management? Can you describe what Quilt is and the story behind it?
How have the goals and features of the Quilt platform changed since I spoke with Kevin in June of 2018?
What are the main problems that users are trying to solve when they find Quilt?
What are some of the alternative approaches/products that they are coming from?
How does Quilt compare with options such as LakeFS, Unstruk, Pachyderm, etc.? Can you describe how Quilt is implemented? What are the types of tools and systems that Quilt gets integrated with?
How do you manage the tension between supporting the lowest common denominator, while providing options for more advanced capabilities?
What is a typical workflow for a team that is using Quilt to manage their data? What are the most interesting, innovative, or unexpected ways that you have seen Quilt used? What are the most interesting, unexpected, or challenging lessons that you have learned while working on Quilt? When is Quilt the wrong choice? What do you have planned for the future of Quilt?
Contact Info
LinkedIn @akarve on Twitter
Parting Question
From your perspective, what is the biggest gap in the tooling or technology for data management today?
Closing Announcements
Thank you for listening! Don't forget to check out our other shows. Podcast.init covers the Python language, its community, and the innovative ways it is being used. The Machine Learning Podcast helps you go from idea to production with machine learning. Visit the site to subscribe to the show, sign up for the mailing list, and read the show notes. If you've learned something or tried out a project from the show then tell us about it! Email [email protected]) with your story. To help other people find the show please leave a review on Apple Podcasts and tell your friends and co-workers
Links
Quilt Data
Podcast Episode
UW Madison Docker Swarm Kaggle open.quiltdata.com FinOS Perspective LakeFS
Podcast Episode
Pachyderm
Podcast Episode
Unstruk
Podcast Episode
Parquet Avro ORC Cloudformation Troposphere CDK == Cloud Development Kit Shadow IT
Podcast Episode
Delta Lake
Podcast Episode
Apache Iceberg
Podcast Episode
Datasette Frictionless DVC
Podcast.init Episode
The in

The focus of this IBM® Blueprint is to showcase a method to store volumes that are created by using Safeguarded Copy off-premise to Amazon S3 object storage that uses the IBM FlashSystem Transparent cloud tiering (TCT) feature. TCT enables volume data to be copied and transferred to object storage. The TCT feature supports creating connections to cloud service providers to store copies of volume data in private or public clouds. This feature is useful for organizations of all sizes when planning for disaster recovery operations or storing a copy of data as extra backup. TCT provides seamless integration between the storage system and public or private clouds for Safeguarded Copy volumes and non-Safeguarded Copy volumes.

Know how to use the new capabilities and cloud integrations in SQL Server 2022. This book covers the many innovative integrations with the Azure Cloud that make SQL Server 2022 the most cloud-connected edition ever. The book covers cutting-edge features such as the blockchain-based Ledger for creating a tamper-evident record of changes to data over time that you can rely on to be correct and reliable. You'll learn about built-in Query Intelligence capabilities to help you to upgrade with confidence that your applications will perform at least as fast after the upgrade than before. In fact, you'll probably see an increase in performance from the upgrade, with no code changes needed. Also covered are innovations such as contained availability groups and data virtualization with S3 object storage. New cloud integrations covered in this book include Microsoft Azure Purview and the use of Azure SQL for high availability and disaster recovery. The bookcovers Azure Synapse Link with its built-in capabilities to take changes and put them into Synapse automatically. Anyone building their career around SQL Server will want this book for the valuable information it provides on building SQL skills from edge to the cloud. What You Will Learn Know how to use all of the new capabilities and cloud integrations in SQL Server 2022 Connect to Azure for disaster recovery, near real-time analytics, and security Leverage the Ledger to create a tamper-evident record of data changes over time Upgrade from prior releases and achieve faster and more consistent performance with no code changes Access data and storage in different and new formats, such as Parquet and S3, without moving the data and using your existing T-SQL skills Explore new application scenarios using innovations with T-SQL in areassuch as JSON and time series Who This Book Is For SQL Server professionals who want to upgrade their skills to the latest edition of SQL Server; those wishing to take advantage of new integrations with Microsoft Azure Purview (governance), Azure Synapse (analytics), and Azure SQL (HA and DR); and those in need of the increased performance and security offered by Query Intelligence and the new Ledger

Apache Kafka is the de facto standard for real-time event streaming, but what do you do if you want to perform user-facing, ad-hoc, real-time analytics too? That's where Apache Pinot comes in.
Apache Pinot is a realtime distributed OLAP datastore, which is used to deliver scalable real time analytics with low latency. It can ingest data from batch data sources (S3, HDFS, Azure Data Lake, Google Cloud Storage) as well as streaming sources such as Kafka. Pinot is used extensively at LinkedIn and Uber to power many analytical applications such as Who Viewed My Profile, Ad Analytics, Talent Analytics, Uber Eats and many more serving 100k+ queries per second while ingesting 1Million+ events per second.
Apache Kafka's highly performant, distributed, fault-tolerant, real-time publish-subscribe messaging platform powers big data solutions at Airbnb, LinkedIn, MailChimp, Netflix, the New York Times, Oracle, PayPal, Pinterest, Spotify, Twitter, Uber, Wikimedia Foundation, and countless other businesses.
Come hear from Neha Power, Founding Engineer at a StarTree and PMC and committer of Apache Pinot, and Karin Wolok, Head of Developer Community at StarTree, on an introduction to both systems and a view of how they work together.
Connect with us: Website: https://databricks.com Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/databricksinc Twitter: https://twitter.com/databricks LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/data... Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/databricksinc/
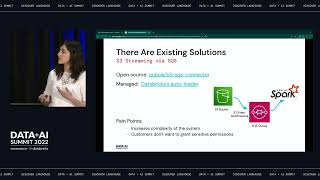
Working with S3 is different from doing so with HDFS: The architecture of the Object store makes the standard Spark file connector inefficient to work with S3.
There is a way to tackle this problem with a message queue for listening to changes in a bucket. What if an additional message queue is not an option and you need to use Spark-streaming? You can use a standard file connector, but you quickly face performance degradation with a number of files in the source path.
We have seen this happen at Hunters, a security operations platform that works with a wide range of data sources.
We want to share a description of the problem and the solution we will open-source. The audience will learn how to configure it and make the best use of it. We will also discuss how to use metadata to boost the performance of discovering new files in the stream and show the use case of utilizing time metadata of CloudTrail to efficiently collect logs for hunting cyber attacks.
Connect with us: Website: https://databricks.com Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/databricksinc Twitter: https://twitter.com/databricks LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/data... Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/databricksinc/

Presto was originally designed to run interactive queries against data warehouses, but now it has evolved into a unified SQL engine on top of open data lake analytics for both interactive and batch workloads. However, Presto doesn't scale to very large and complex batch pipelines. Presto Unlimited was designed to address such scalability challenges but it didn’t fully solve fault tolerance, isolation, and resource management.
Spark is the tool of choice across the industry for running large scale complex batch ETL pipelines. This motivated the development of Presto On Spark. Presto on Spark runs Presto as a library that is submitted with spark-submit to a Spark cluster. It leverages Spark for scaling shuffle, worker execution, and resource management. It thereby eliminates any query conversion between interactive and batch use cases. This solution helps enable a performant and scalable platform with seamless end-to-end experience to explore and process data.
Many analysts at Intuit use Presto to explore data in the Data Lake/S3 and use Spark for batch processing. These analysts would earlier spend several hours converting these exploration SQLs written for Presto to Spark SQL to operationalize/schedule them as data pipelines. Presto On Spark is now used by analysts at Intuit to run thousands of critical jobs. No query conversion is required here, improved analysts' productivity and empowered them to deliver insights at high speed.
Benefits from session: Attendees will learn about Presto On Spark architecture Attendees will learn when To Use Spark's Execution Engine With Presto Attendees will learn how Intuit runs thousands of presto jobs daily leveraging databricks platform which they can apply to their own work
Connect with us: Website: https://databricks.com Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/databricksinc Twitter: https://twitter.com/databricks LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/data... Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/databricksinc/

In general , in-memory pipelines would scale quite well in Spark if we apply the same processing logic to all records. But for Salesforce the major challenge is, we need to apply custom logic specific to a Log Record Type (LRT). The custom logic includes applying different schemas while processing each event. So performing such custom logic specific to LRT , we need to have a mechanism to collect LRT specific data In-Memory such that we can apply custom logic to each collection. We normally get around 50K files in S3 every 5 minutes and there are around 4 billion log events there in 50K files. Creating a DataFrame from 50K files, then group events by LRTs and applying filters per LRT to create a child DataFrame is one approach. One major challenge is that LRT data distribution is very skewed , so we need an efficient in-memory partitioning strategy to distribute the data. Also just applying filters on parent DataFrame will have many child Data frames with empty partitions due to large skew in data distribution and this creates too many empty tasks while processing child DataFrames. So we need to have a Partitioning schema to distribute data and filter by Log Type but not create unnecessary empty partitions in child DataFrames. We also need a scheduling algorithm to process all child DataFrames to utilize cluster efficiency. We have implemented a custom Spark Streaming for reading SQS notifications and then reading new files in S3 which is designed to scale with ingestion volume . This talk will cover how we performed a Spark RangePartition based on Size distribution of the incoming data and applying schema specific transformation logic. This talk will explain various optimizations at various stages of the processing to meet our latency goal.
Connect with us: Website: https://databricks.com Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/databricksinc Twitter: https://twitter.com/databricks LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/data... Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/databricksinc/
Scribd's data architecture was originally batch-oriented, but in the last couple years, we introduced streaming data ingestion to provide near-real-time ad hoc query capability, mitigate the need for more batch processing tasks, and set the foundation for building real-time data applications.
Kafka and Delta Lake are the two key components of our streaming ingestion pipeline. Various applications and services write messages to Kafka as events are happening. We were tasked with getting these messages into Delta Lake quickly and efficiently.
Our first solution was to deploy Spark Structured Streaming jobs. This got us off the ground quickly, but had some downsides.
Since Delta Lake and the Delta transaction protocol are open source, we kicked off a project to implement our own Rust ingestion daemon. We were confident we could deliver a Rust implementation since our ingestion jobs are append only. Rust offers high performance with a focus on code safety and modern syntax.
In this talk I will describe Scribd's unique approach to ingesting messages from Kafka topics into Delta Lake tables. I will describe the architecture, deployment model, and performance of our solution, which leverages the kafka-delta-ingest Rust daemon and the delta-rs crate hosted in auto-scaling ECS services. I will discuss foundational design aspects for achieving data integrity such as distributed locking with DynamoDb to overcome S3's lack of "PutIfAbsent" semantics, and avoiding duplicates or data loss when multiple concurrent tasks are handling the same stream. I'll highlight the reliability and performance characteristics we've observed so far. I'll also describe the Terraform deployment model we use to deliver our 70-and-growing production ingestion streams into AWS.
Connect with us: Website: https://databricks.com Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/databricksinc Twitter: https://twitter.com/databricks LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/data... Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/databricksinc/

In the past, stream processing over data lakes required a lot of development efforts from data engineering teams, as Itai has shown in his talk at Spark+AI Summit 2019 (https://tinyurl.com/2s3az5td). Today, with Delta Lake and Databricks Auto Loader, this becomes a few minutes' work! Not only that, it unlocks a new set of ways to efficiently leverage your data.
Nexar, a leading provider of dynamic mapping solutions, utilizes Delta Lake and advanced features such as Auto Loader to map 150 million miles of roads a month and provide meaningful insights to cities, mobility companies, driving apps, and insurers. Nexar’s growing dataset contains trillions of images that are used to build and maintain a digital twin of the world. Nexar uses state-of-the-art technologies to detect road furniture (like road signs and traffic lights), surface markings, and road works.
In this talk, we will describe how you can efficiently ingest, process, and maintain a robust Data Lake, whether you’re a mapping solutions provider, a media measurement company, or a social media network. Topics include: * Incremental & efficient streaming over cloud storage such as S3 * Storage optimizations using Delta Lake * Supporting mutable data use-cases with Delta Lake
Connect with us: Website: https://databricks.com Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/databricksinc Twitter: https://twitter.com/databricks LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/data... Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/databricksinc/

The Delta ecosystem rapidly expanded with the release of Delta Lake 1.2 which included integrations with Apache Spark™, Apache Flink, Presto, Trino, features such as OPTIMIZE, data skipping using column statistics, restore APIs, S3 multi-cluster writes, and more.
Join this session to learn about how the wider Delta community collaborated together to bring these features and integrations together; as well as the current roadmap. This will be an interactive session so come prepared with your questions—we should have answers!
Connect with us: Website: https://databricks.com Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/databricksinc Twitter: https://twitter.com/databricks LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/data... Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/databricksinc/

Rust guarantees zero memory access bug once a program compiles. However, one can still introduce logical bugs in the implementation.
In this talk, I will first give a high level overview on common formal verification methods used in distributed system designs and implementations. Then I will talk about our experiences with using TLA+ and Stateright to formally model delta-rs' multi-writer S3 backend implementation. The end result of combining both Rust and formal verification is we end up with an efficient native Delta Lake implementation that is both memory safe and logical bug free!
Connect with us: Website: https://databricks.com Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/databricksinc Twitter: https://twitter.com/databricks LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/data... Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/databricksinc/

After three years of hard work by the Delta community, we are proud to announce the release of Delta Lake 2.0. Completing the work to open-source all of Delta Lake while tens of thousands of organizations were running in production was no small feat and we have the ever-expanding Delta community to thank! Join this session to learn about how the wider Delta community collaborated together to bring these features and integrations together.
Join this session to learn about how the wider Delta community collaborated together to bring these features and integrations together. This includes the Integrations with Apache Spark™, Apache Flink, Apache Pulsar, Presto, Trino, and more.
Features such as OPTIMIZE ZORDER, data skipping using column stats, S3 multi-cluster writes, Change Data Feed, and more.
Language APIs including Rust, Python, Ruby, GoLang, Scala, and Java.
Connect with us: Website: https://databricks.com Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/databricksinc Twitter: https://twitter.com/databricks LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/data... Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/databricksinc/