Unlock the Power of Fine-Tuning with Apps Script! Learn how to optimize pre-trained models for specific tasks using Google Apps Script. This session covers exporting data from Sheets to Cloud Storage as JSONL, building an Apps Script prompt explainer backend, and creating service accounts for secure access to Vertex AI and Cloud Storage. We'll also show how to collect, transform, and split data for training, launch the fine-tuning process, and test results in Vertex AI and a Google Chat bot. Master fine-tuning for practical AI applications.
 talk-data.com
talk-data.com
Topic
Cloud Storage
67
tagged
Activity Trend
Top Events
Kir Titievsky, Product Manager at Google Cloud with extensive experience in streaming and storage infrastructure, joined Yuliia and Dumky to talk about streaming. Drawing from his work with Apache Kafka, Cloud PubSub, Dataflow and Cloud Storage since 2015, Kir explains the fundamental differences between streaming and micro-batch processing. He challenges common misconceptions about streaming costs, explaining how streaming can be significantly less expensive than batch processing for many use cases. Kir shares insights on the "service bus architecture" revival, discussing how modern distributed messaging systems have solved historic bottlenecks while creating new opportunities for business and performance needs.Kir's medium - https://medium.com/@kir-gcpKir's Linkedin page - https://www.linkedin.com/in/kir-titievsky-%F0%9F%87%BA%F0%9F%87%A6-7775052/

🌟 Session Overview 🌟
Session Name: Insights into Your Cloud Database: How Storage Engines Actually Work Speaker: Jan Mensch Session Description: In this session, we will dive into the inner workings of cloud storage engines by exploring Hummock, the storage engine behind RisingWave, a streaming database. We will cover how data writes occur in Hummock, focusing on the crucial role of MemTables in managing data before persistence. You will gain an understanding of Log-Structured Merge (LSM) trees and their importance in optimizing both read and write performance. Additionally, we will explore the function of L0 sublevels in accelerating the compaction process. We’ll discuss Sorted String Tables (SSTs), including how they organize data, their versioning, and how this versioning connects to distributed snapshots in streaming systems. Furthermore, we will examine the necessity of compaction and how it represents a trade-off between read and write amplification. By the end of the session, you will gain valuable insights into the mechanics of LSM storage engines and their role in powering streaming databases. 🚀 About Big Data and RPA 2024 🚀
Unlock the future of innovation and automation at Big Data & RPA Conference Europe 2024! 🌟 This unique event brings together the brightest minds in big data, machine learning, AI, and robotic process automation to explore cutting-edge solutions and trends shaping the tech landscape. Perfect for data engineers, analysts, RPA developers, and business leaders, the conference offers dual insights into the power of data-driven strategies and intelligent automation. 🚀 Gain practical knowledge on topics like hyperautomation, AI integration, advanced analytics, and workflow optimization while networking with global experts. Don’t miss this exclusive opportunity to expand your expertise and revolutionize your processes—all from the comfort of your home! 📊🤖✨
📅 Yearly Conferences: Curious about the evolution of QA? Check out our archive of past Big Data & RPA sessions. Watch the strategies and technologies evolve in our videos! 🚀 🔗 Find Other Years' Videos: 2023 Big Data Conference Europe https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLqYhGsQ9iSEpb_oyAsg67PhpbrkCC59_g 2022 Big Data Conference Europe Online https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLqYhGsQ9iSEryAOjmvdiaXTfjCg5j3HhT 2021 Big Data Conference Europe Online https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLqYhGsQ9iSEqHwbQoWEXEJALFLKVDRXiP
💡 Stay Connected & Updated 💡
Don’t miss out on any updates or upcoming event information from Big Data & RPA Conference Europe. Follow us on our social media channels and visit our website to stay in the loop!
🌐 Website: https://bigdataconference.eu/, https://rpaconference.eu/ 👤 Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/bigdataconf, https://www.facebook.com/rpaeurope/ 🐦 Twitter: @BigDataConfEU, @europe_rpa 🔗 LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/73234449/admin/dashboard/, https://www.linkedin.com/company/75464753/admin/dashboard/ 🎥 YouTube: http://www.youtube.com/@DATAMINERLT
Summary The rapid growth of generative AI applications has prompted a surge of investment in vector databases. While there are numerous engines available now, Lance is designed to integrate with data lake and lakehouse architectures. In this episode Weston Pace explains the inner workings of the Lance format for table definitions and file storage, and the optimizations that they have made to allow for fast random access and efficient schema evolution. In addition to integrating well with data lakes, Lance is also a first-class participant in the Arrow ecosystem, making it easy to use with your existing ML and AI toolchains. This is a fascinating conversation about a technology that is focused on expanding the range of options for working with vector data. Announcements Hello and welcome to the Data Engineering Podcast, the show about modern data managementImagine catching data issues before they snowball into bigger problems. That’s what Datafold’s new Monitors do. With automatic monitoring for cross-database data diffs, schema changes, key metrics, and custom data tests, you can catch discrepancies and anomalies in real time, right at the source. Whether it’s maintaining data integrity or preventing costly mistakes, Datafold Monitors give you the visibility and control you need to keep your entire data stack running smoothly. Want to stop issues before they hit production? Learn more at dataengineeringpodcast.com/datafold today!Your host is Tobias Macey and today I'm interviewing Weston Pace about the Lance file and table format for column-oriented vector storageInterview IntroductionHow did you get involved in the area of data management?Can you describe what Lance is and the story behind it?What are the core problems that Lance is designed to solve?What is explicitly out of scope?The README mentions that it is straightforward to convert to Lance from Parquet. What is the motivation for this compatibility/conversion support?What formats does Lance replace or obviate?In terms of data modeling Lance obviously adds a vector type, what are the features and constraints that engineers should be aware of when modeling their embeddings or arbitrary vectors?Are there any practical or hard limitations on vector dimensionality?When generating Lance files/datasets, what are some considerations to be aware of for balancing file/chunk sizes for I/O efficiency and random access in cloud storage?I noticed that the file specification has space for feature flags. How has that aided in enabling experimentation in new capabilities and optimizations?What are some of the engineering and design decisions that were most challenging and/or had the biggest impact on the performance and utility of Lance?The most obvious interface for reading and writing Lance files is through LanceDB. Can you describe the use cases that it focuses on and its notable features?What are the other main integrations for Lance?What are the opportunities or roadblocks in adding support for Lance and vector storage/indexes in e.g. Iceberg or Delta to enable its use in data lake environments?What are the most interesting, innovative, or unexpected ways that you have seen Lance used?What are the most interesting, unexpected, or challenging lessons that you have learned while working on the Lance format?When is Lance the wrong choice?What do you have planned for the future of Lance?Contact Info LinkedInGitHubParting Question From your perspective, what is the biggest gap in the tooling or technology for data management today?Links Lance FormatLanceDBSubstraitPyArrowFAISSPineconePodcast EpisodeParquetIcebergPodcast EpisodeDelta LakePodcast EpisodePyLanceHilbert CurvesSIFT VectorsS3 ExpressWekaDataFusionRay DataTorch Data LoaderHNSW == Hierarchical Navigable Small Worlds vector indexIVFPQ vector indexGeoJSONPolarsThe intro and outro music is from The Hug by The Freak Fandango Orchestra / CC BY-SA

As enterprises adopt generative AI, one of the biggest challenges is understanding security for data models and preventing unauthorized disclosure of sensitive data. When data models contain malicious code or output sensitive information, it can put enterprises at risk. In this lightning talk, explore GenAI Secure by Cloud Storage Security, which is designed to help organizations secure both data models used by services like Amazon Bedrock or Amazon SageMaker and outputs like text or chats produced by generative AI applications. Come learn how to deploy GenAI Secure and quickly quarantine malicious code and sensitive data exposed to your generative AI application. This presentation is brought to you by Cloud Storage Security, an AWS Partner.
Learn more about AWS re:Inforce at https://go.aws/reinforce.
Subscribe: More AWS videos: http://bit.ly/2O3zS75 More AWS events videos: http://bit.ly/316g9t4
ABOUT AWS Amazon Web Services (AWS) hosts events, both online and in-person, bringing the cloud computing community together to connect, collaborate, and learn from AWS experts.
AWS is the world's most comprehensive and broadly adopted cloud platform, offering over 200 fully featured services from data centers globally. Millions of customers—including the fastest-growing startups, largest enterprises, and leading government agencies—are using AWS to lower costs, become more agile, and innovate faster.
reInforce2024 #CloudSecurity #AWS #AmazonWebServices #CloudComputing
Unifying storage for your data analytics workloads doesn‘t have to be hard. See how Google Cloud Storage brings your data closer to compute and meets your applications where they are, all while achieving exabyte scale, strong consistency, and lower costs. You'll get new product announcements and see enterprise customers present real-world solutions using Cloud Storage with BigQuery, Hadoop, Spark, Kafka, and more.
Click the blue “Learn more” button above to tap into special offers designed to help you implement what you are learning at Google Cloud Next 25.
As generative AI applications mature, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has become popular for improving large language model-based apps. We expect teams to move beyond basic RAG to autonomous agents and generative loops. We'll set up a Weaviate vector database on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) and Gemini to showcase generative feedback loops.
After this session, a Google Cloud GKE user should be able to:
- Deploy Weaviate open source on GKE
- Set up a pipeline to ingest data from the Cloud Storage bucket
- Query, RAG, and enhance the responses
Click the blue “Learn more” button above to tap into special offers designed to help you implement what you are learning at Google Cloud Next 25.
This session is for AI/ML and data practitioners who want to build AI/ML data pipelines at scale and select the right combination of block, file, and object storage solution for your use case. Learn how to optimize all your AI/ML workloads like data preparation, training, tuning, inference, and serving with the best storage solution and easily integrate them into your Compute Engine, Google Kubernetes Engine, or Vertex workflows. We’ll also dive into how to optimize analytics workloads with Cloud Storage and Anywhere Cache.
Click the blue “Learn more” button above to tap into special offers designed to help you implement what you are learning at Google Cloud Next 25.
Attend this session for an overview of our storage solutions and how they are optimized for a variety of workloads. We’ll share storage best practices for AI, Google Kubernetes Engine, and VMs, and customer storage and infrastructure cost optimization. You’ll gain insight into new features that deliver more performant and available apps to your business. We’ll also share our storage vision providing you the ability to plan for future application workloads.
-Industry’s first unified cloud storage optimized for AI and analytics workloads;
-Intelligent storage powered by AI;
-Built for mission-critical, high-availability data protection;
-Migrating to cloud storage and Google Cloud at scale at low cost
Click the blue “Learn more” button above to tap into special offers designed to help you implement what you are learning at Google Cloud Next 25.
Learn how Google Cloud’s backup and storage services secure and protect your data from a variety of threats, such as ransomware, outages, and user errors. Our backup services protect VMs, databases (such as SAP HANA), and Google Kubernetes Engine environments. Expand threat detection capabilities by alerting on suspicious activities around backup through Security Command Center. We’ll also dive into Cloud Storage and our industry-leading turbo replication for dual-region deployments, soft delete, versioning, and more to protect your data.
Click the blue “Learn more” button above to tap into special offers designed to help you implement what you are learning at Google Cloud Next 25.
Introduces new GCS management features and shares best practices to solve customers' goals of cost optimization, security and governance at billions of objects scale. Demos and details of Storage Insights Datasets, generating insights with Gemini and new data movement feature. Plus, learn directly from Recursion Pharma about their real-world success managing Cloud Storage at scale.
Click the blue “Learn more” button above to tap into special offers designed to help you implement what you are learning at Google Cloud Next 25.
Migrating high performance computing (HPC) workloads to the cloud presents unique challenges, as traditional on-premises infrastructure often clashes with cloud architectures, leading to operational and cost inefficiencies. Embracing core technologies like Google Kubernetes Engine and Google Cloud Storage offers a compelling solution to these hurdles. In this session, we explore PGS the transition of our entire HPC system to Google Cloud. This move allows us to run workloads five times larger than previously possible while reducing turnaround time by a factor of two.
Click the blue “Learn more” button above to tap into special offers designed to help you implement what you are learning at Google Cloud Next 25.

This IBM Redbooks® publication covers IBM TS7700 R5.3. The IBM TS7700 is part of a family of IBM Enterprise tape products. This book is intended for system architects and storage administrators who want to integrate their storage systems for optimal operation. Building on over 25 years of experience, the R5.3 release includes many features that enable improved performance, usability, and security. Highlights include the IBM TS7700 Advanced Object Store, an all flash TS7770, grid resiliency enhancements, and Logical WORM retention. By using the same hierarchical storage techniques, the TS7700 (TS7770 and TS7760) can also off load to object storage. Because object storage is cloud-based and accessible from different regions, the TS7700 Cloud Storage Tier support essentially allows the cloud to be an extension of the grid. As of this writing, the TS7700C supports the ability to off load to IBM Cloud Object Storage, Amazon S3, and RSTOR. This publication explains features and concepts that are specific to the IBM TS7700 as of release R5.3. The R5.3 microcode level provides IBM TS7700 Cloud Storage Tier enhancements, IBM DS8000 Object Storage enhancements, Management Interface dual control security, and other smaller enhancements. The R5.3 microcode level can be installed on the IBM TS7770 and IBM TS7760 models only. TS7700 provides tape virtualization for the IBM Z® environment. Off loading to physical tape behind a TS7700 is used by hundreds of organizations around the world. New and existing capabilities of the TS7700 5.3 release includes the following highlights: Support for IBM TS1160 Tape Drives and JE/JM media Eight-way Grid Cloud, which consists of up to three generations of TS7700 Synchronous and asynchronous replication of virtual tape and TCT objects Grid access to all logical volume and object data independent of where it resides An all flash TS7770 option for improved performance Full Advanced Object Store Grid Cloud support of DS8000 Transparent Cloud Tier Full AES256 encryption for data that is in-flight and at-rest Tight integration with IBM Z and DFSMS policy management DS8000 Object Store with AES256 in-flight encryption and compression Regulatory compliance through Logical WORM and LWORM Retention support Cloud Storage Tier support for archive, logical volume versions, and disaster recovery Optional integration with physical tape 16 Gb IBM FICON® throughput that exceeds 4 GBps per TS7700 cluster Grid Resiliency Support with Control Unit Initiated Reconfiguration (CUIR) support IBM Z hosts view up to 3,968 3490 devices per TS7700 grid TS7770 Cache On Demand feature that uses capacity-based licensing TS7770 support of SSD within the VED server The TS7700T writes data by policy to physical tape through attachment to high-capacity, high-performance IBM TS1160, IBM TS1150, and IBM TS1140 tape drives that are installed in an IBM TS4500 or TS3500 tape library. The TS7770 models are based on high-performance and redundant IBM Power9® technology. They provide improved performance for most IBM Z tape workloads when compared to the previous generations of IBM TS7700.

This book is your practical and comprehensive guide to learning Google Cloud Platform (GCP) for data science, using only the free tier services offered by the platform. Data science and machine learning are increasingly becoming critical to businesses of all sizes, and the cloud provides a powerful platform for these applications. GCP offers a range of data science services that can be used to store, process, and analyze large datasets, and train and deploy machine learning models. The book is organized into seven chapters covering various topics such as GCP account setup, Google Colaboratory, Big Data and Machine Learning, Data Visualization and Business Intelligence, Data Processing and Transformation, Data Analytics and Storage, and Advanced Topics. Each chapter provides step-by-step instructions and examples illustrating how to use GCP services for data science and big data projects. Readers will learn how to set up a Google Colaboratory account and run Jupyternotebooks, access GCP services and data from Colaboratory, use BigQuery for data analytics, and deploy machine learning models using Vertex AI. The book also covers how to visualize data using Looker Data Studio, run data processing pipelines using Google Cloud Dataflow and Dataprep, and store data using Google Cloud Storage and SQL. What You Will Learn Set up a GCP account and project Explore BigQuery and its use cases, including machine learning Understand Google Cloud AI Platform and its capabilities Use Vertex AI for training and deploying machine learning models Explore Google Cloud Dataproc and its use cases for big data processing Create and share data visualizations and reports with Looker Data Studio Explore Google Cloud Dataflow and its use cases for batch and stream data processing Run data processing pipelines on Cloud Dataflow Explore Google Cloud Storageand its use cases for data storage Get an introduction to Google Cloud SQL and its use cases for relational databases Get an introduction to Google Cloud Pub/Sub and its use cases for real-time data streaming Who This Book Is For Data scientists, machine learning engineers, and analysts who want to learn how to use Google Cloud Platform (GCP) for their data science and big data projects

IBM® Storage as a Service (STaaS) extends your hybrid cloud experience with a new flexible consumption model enabled for both your on-premises and hybrid cloud infrastructure needs, giving you the agility, cash flow efficiency, and services of cloud storage with the flexibility to dynamically scale up or down and only pay for what you use beyond the minimal capacity. This IBM Redpaper provides a detailed introduction to the IBM STaaS service. The paper is targeted for data center managers and storage administrators.
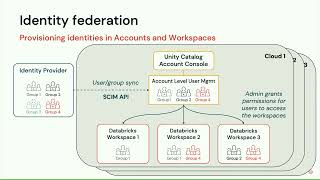
Across industries, a multicloud setup has quickly become the reality for large organizations. Multi-cloud introduces new governance challenges as permissions models often do not translate from one cloud to the other and if they do, are insufficiently granular to accommodate privacy requirements and principles of least privilege. This problem can be especially acute for data and AI workloads that rely on sharing and aggregating large and diverse data sources across business unit boundaries and where governance models need to incorporate assets such as table rows/columns and ML features and models.
In this session, we will provide guidelines on how best to overcome these challenges for companies that have adopted the Databricks Lakehouse as their collaborative space for data teams across the organization, by exploiting some of the unique product features of the Databricks platform. We will focus on a common scenario: a data platform team providing data assets to two different ML teams, one using the same cloud and the other one using a different cloud.
We will explain the step-by-step setup of a unified governance model by leveraging the following components and conventions:
- Unity Catalog for implementing fine-grained access control across all data assets: files in cloud storage, rows and columns in tables and ML features and models
- The Databricks Terraform provider to automatically enforce guardrails and permissions across clouds
- Account level SSO Integration and identity federation to centralize administer access across workspaces
- Delta sharing to seamlessly propagate changes in provider data sets to consumers in near real-time
- Centralized audit logging for a unified view on what asset was accessed by whom
Talk by: Ioannis Papadopoulos and Volker Tjaden
Connect with us: Website: https://databricks.com Twitter: https://twitter.com/databricks LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/databricks Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/databricksinc Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/databricksinc

Vector databases such as ElasticSearch and Pinecone offer fast ingestion and querying on vector embeddings with ANNs. However, they typically do not decouple compute and storage, making them hard to integrate in production data stacks. Because data storage in these databases is expensive and not easily accessible, data teams typically maintain ETL pipelines to offload historical embedding data to blob stores. When that data needs to be queried, they get loaded back into the vector database in another ETL process. This is reminiscent of loading data from OLTP database to cloud storage, then loading said data into an OLAP warehouse for offline analytics.
Recently, “lakehouse” offerings allow direct OLAP querying on cloud storage, removing the need for the second ETL step. The same could be done for embedding data. While embedding storage in blob stores cannot satisfy the high TPS requirements in online settings, we argue it’s sufficient for offline analytics use cases like slicing and dicing data based on embedding clusters. Instead of loading the embedding data back into the vector database for offline analytics, we propose direct processing on embeddings stored in Parquet files in Delta Lake. You will see that offline embedding workloads typically touch a large portion of the stored embeddings without the need for random access.
As a result, the workload is entirely bound by network throughput instead of latency, making it quite suitable for blob storage backends. On a test one billion vector dataset, ETL into cloud storage takes around one hour on a dedicated GPU instance, while batched nearest neighbor search can be done in under one minute with four CPU instances. We believe future “lakehouses” will ship with native support for these embedding workloads.
Talk by: Tony Wang and Chang She
Here’s more to explore: State of Data + AI Report: https://dbricks.co/44i2HBp Databricks named a Leader in 2022 Gartner® Magic QuadrantTM CDBMS: https://dbricks.co/3phw20d
Connect with us: Website: https://databricks.com Twitter: https://twitter.com/databricks LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/databricks Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/databricksinc Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/databricksinc

Apache Kafka is the de facto standard for real-time event streaming, but what do you do if you want to perform user-facing, ad-hoc, real-time analytics too? That's where Apache Pinot comes in.
Apache Pinot is a realtime distributed OLAP datastore, which is used to deliver scalable real time analytics with low latency. It can ingest data from batch data sources (S3, HDFS, Azure Data Lake, Google Cloud Storage) as well as streaming sources such as Kafka. Pinot is used extensively at LinkedIn and Uber to power many analytical applications such as Who Viewed My Profile, Ad Analytics, Talent Analytics, Uber Eats and many more serving 100k+ queries per second while ingesting 1Million+ events per second.
Apache Kafka's highly performant, distributed, fault-tolerant, real-time publish-subscribe messaging platform powers big data solutions at Airbnb, LinkedIn, MailChimp, Netflix, the New York Times, Oracle, PayPal, Pinterest, Spotify, Twitter, Uber, Wikimedia Foundation, and countless other businesses.
Come hear from Neha Power, Founding Engineer at a StarTree and PMC and committer of Apache Pinot, and Karin Wolok, Head of Developer Community at StarTree, on an introduction to both systems and a view of how they work together.
Connect with us: Website: https://databricks.com Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/databricksinc Twitter: https://twitter.com/databricks LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/data... Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/databricksinc/

In the past, stream processing over data lakes required a lot of development efforts from data engineering teams, as Itai has shown in his talk at Spark+AI Summit 2019 (https://tinyurl.com/2s3az5td). Today, with Delta Lake and Databricks Auto Loader, this becomes a few minutes' work! Not only that, it unlocks a new set of ways to efficiently leverage your data.
Nexar, a leading provider of dynamic mapping solutions, utilizes Delta Lake and advanced features such as Auto Loader to map 150 million miles of roads a month and provide meaningful insights to cities, mobility companies, driving apps, and insurers. Nexar’s growing dataset contains trillions of images that are used to build and maintain a digital twin of the world. Nexar uses state-of-the-art technologies to detect road furniture (like road signs and traffic lights), surface markings, and road works.
In this talk, we will describe how you can efficiently ingest, process, and maintain a robust Data Lake, whether you’re a mapping solutions provider, a media measurement company, or a social media network. Topics include: * Incremental & efficient streaming over cloud storage such as S3 * Storage optimizations using Delta Lake * Supporting mutable data use-cases with Delta Lake
Connect with us: Website: https://databricks.com Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/databricksinc Twitter: https://twitter.com/databricks LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/data... Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/databricksinc/

Auto loader, the most popular tool for incremental data ingestion from cloud storage to Databricks’ Lakehouse, is used in our biggest customers’ ingestion workflows. Auto Loader is our all-in-one solution for exactly-once processing offering efficient file discovery, schema inference and evolution, and fault tolerance.
In this talk, we want to delve into key features in Auto Loader, including: • Avro schema inference • Rescued column • Semi-structured data support • Incremental listing • Asynchronous backfilling • Native listing • File-level tracking and observability
Auto Loader is also used in other Databricks features such as Delta Live Tables. We will discuss the architecture, provide a demo, and feature an Auto Loader customer speaking about their experience migrating to Auto Loader.
Connect with us: Website: https://databricks.com Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/databricksinc Twitter: https://twitter.com/databricks LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/data... Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/databricksinc/