Summary
Building an ETL pipeline is a common need across businesses and industries. It’s easy to get one started but difficult to manage as new requirements are added and greater scalability becomes necessary. Rather than duplicating the efforts of other engineers it might be best to use a hosted service to handle the plumbing so that you can focus on the parts that actually matter for your business. In this episode CTO and co-founder of Alooma, Yair Weinberger, explains how the platform addresses the common needs of data collection, manipulation, and storage while allowing for flexible processing. He describes the motivation for starting the company, how their infrastructure is architected, and the challenges of supporting multi-tenancy and a wide variety of integrations.
Preamble
Hello and welcome to the Data Engineering Podcast, the show about modern data management
When you’re ready to build your next pipeline you’ll need somewhere to deploy it, so check out Linode. With private networking, shared block storage, node balancers, and a 40Gbit network, all controlled by a brand new API you’ve got everything you need to run a bullet-proof data platform. Go to dataengineeringpodcast.com/linode to get a $20 credit and launch a new server in under a minute.
For complete visibility into the health of your pipeline, including deployment tracking, and powerful alerting driven by machine-learning, DataDog has got you covered. With their monitoring, metrics, and log collection agent, including extensive integrations and distributed tracing, you’ll have everything you need to find and fix performance bottlenecks in no time. Go to dataengineeringpodcast.com/datadog today to start your free 14 day trial and get a sweet new T-Shirt.
Go to dataengineeringpodcast.com to subscribe to the show, sign up for the newsletter, read the show notes, and get in touch.
Your host is Tobias Macey and today I’m interviewing Yair Weinberger about Alooma, a company providing data pipelines as a service
Interview
Introduction
How did you get involved in the area of data management?
What is Alooma and what is the origin story?
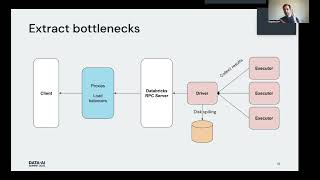
How is the Alooma platform architected?
I want to go into stream VS batch here
What are the most challenging components to scale?
How do you manage the underlying infrastructure to support your SLA of 5 nines?
What are some of the complexities introduced by processing data from multiple customers with various compliance requirements?
How do you sandbox user’s processing code to avoid security exploits?
What are some of the potential pitfalls for automatic schema management in the target database?
Given the large number of integrations, how do you maintain the
What are some challenges when creating integrations, isn’t it simply conforming with an external API?
For someone getting started with Alooma what does the workflow look like?
What are some of the most challenging aspects of building and maintaining Alooma?
What are your plans for the future of Alooma?
Contact Info
LinkedIn
@yairwein on Twitter
Parting Question
From your perspective, what is the biggest gap in the tooling or technology for data management today?
Links
Alooma
Convert Media
Data Integration
ESB (Enterprise Service Bus)
Tibco
Mulesoft
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load)
Informatica
Microsoft SSIS
OLAP Cube
S3
Azure Cloud Storage
Snowflake DB
Redshift
BigQuery
Salesforce
Hubspot
Zendesk
Spark
The Log: What every software engineer should know about real-time data’s unifying abstraction by Jay Kreps
RDBMS (Relational Database Management System)
SaaS (Software as a Service)
Change Data Capture
Kafka
Storm
Google Cloud PubSub
Amazon Kinesis
Alooma Code Engine
Zookeeper
Idempotence
Kafka Streams
Kubernetes
SOC2
Jython
Docker
Python
Javascript
Ruby
Scala
PII (Personally Identifiable Information)
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
Amazon EMR (Elastic Map Reduce)
Sequoia Capital
Lightspeed Investors
Redis
Aerospike
Cassandra
MongoDB
The intro and outro music is from The Hug by The Freak Fandango Orchestra / CC BY-SA
Support Data Engineering Podcast